NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
1. Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic
field near a long straight wire?
(a) The field consists of
straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(b) The field consists of
straight lines parallel to the wire.
(c) The field consists of
radial lines originating from the wire.
(d) The field consists of
concentric circles centered on the wire.
Ans. (d) The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire.
2. The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
(a) the process of charging a
body.
(b) the process of generating
magnetic field due to a current passing through a coil.
(c) producing induced current
in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
(d) the process of rotating a
coil of an electric motor.
Ans. (d) The process of rotating a coil of an electric motor.
3. The device used for producing electric current is called a
(a)
generator (h)
galvanometer
(c)
ammeter: (d)
motor.
Ans. (a) generator
4. The essential difference between an AC generator and a DC
generator is that
(a) AC generator has an
electromagnet while a DC generator has permanent magnet.
(b) DC generator will generate
a higher voltage.
(c) AC generator will generate
a higher voltage.
(d) AC generator has split
rings while the DC generator has a commutator
Ans. (d) AC generator has split rings while the DC generator has a
commutator.
5. At the time of short circuit the current in the circuit
(a) reduces
substantially. (b)
does not change.
(c) increases
heavily. (d)
Vary continuously.
Ans. (c) increases heavily.
6. State whether the following statements are true or false.
(a) An electric motor converts
mechanical energy into electrical energy.
(b) An electric generator
works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
(c) The field at the centre of
a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines.
(d) A wire with a green
insulation is usually the live wire of an electric supply.
Ans. (a)
False (b)
True
(c)
True (d)
False.
7. List two methods of producing magnetic fields.
Ans. Magnetic field can be produced by any of the following methods:
(i) Any magnet-bar magnet,
horse-shoe magnet or round magnet can be used.
(ii) A wire carrying current
produces a field around it.
(iii) A loop or solenoid
carrying current.
8. How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine
the north and south poles of a current-carrying solenoid with the help of a
liar magnet? Explain.
Ans. A coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped
closely in the shape of a cylinder is called a solenoid. One end of the
solenoid behaves as a magnetic north pole, while the other end behaves as the
south pole. The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel
straight lines. By taking a bar-magnet with known north poles near one end of
the solenoid and if it shows repulsion then that end of solenoid is north pole
and the other end is south pole. The property of magnet i.e. like poles repel
and unlike poles attract is used for the determination of poles of solenoid.
9. When is the force experienced by a current carrying
conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
Ans. According to Flemings left hand rule the force experienced by a
current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is largest when they both
are perpendicular to each other.
10. Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to
one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the
front wall is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is
the direction of magnetic field?
Ans. According to Fleming’s left hand rule, the direction of magnetic
field is downwards.
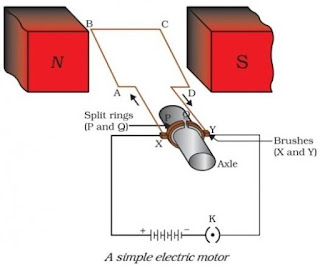
11. Draw a labelled diagram of an electric motor. Explain its
principle and working. What is the function of a split ring in an electric
motor?
Ans.
Principle: A
current carrying conductor when placed at right angle to a magnetic field,
experiences a force due to a which we get motion. The direction of the force is
given by Fleming’s left hand rule.
Working: Current
in the coil ABCD enters from the source battery through conducting brush X and
flows back to the battery through Y. The current flows from arm A to B arm and
then C to D, the direction of flow of current in both arms is opposite. As per
Fleming’s left hand rule, the force acting on arm AB pushes it down while the
force acting on CD pushes it upwards. Thus, the coil and the axle rotate
anticlockwise. Due to action of split ring commutator at half rotation, split
rings P and Q change their contacts with brushes. Now P makes contact with Y
and Q with X. As a result, current begins to flow in coil along DCBA, As a
result now arm AB is being pushed upward and arm CD downward by the magnetic
force. So coil rotate half a turn more in the same direction. This reversing of
current direction is repeated at each half rotation and so the coil continues
to rotate in the same direction. The split ring helps in changing the direction
of the current.
12. Name some devices in which electric motors are used.
Ans. Electric motor is used in all such devices where electric energy
is used, converted into mechanical energy to get the motion of machine. E.g. it
is used in electric fans, mixer grinders, coolers, A.C., washing machines,
computers etc.
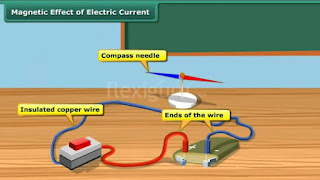
13. A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a
galvanometer; What will happen if a bar magnet is (i) pushed into the coil (ii)
withdrawn from inside the coil (iii) held stationary inside the coil?
Ans. (i) If bar magnet is pushed into the coil of insulated copper
wire, galvanometer shows the deflection as current is induced in the coil.
(ii) When the bar magnet is
withdrawn from the coil the galvanometer shows deflection again but now to the
opposite side.
(iii) When the bar magnet is
held stationary inside the coil, the galvanometer does not show any deflection
no induced current.
14. Two circular coils A and B are placed close to each other If
the current in the coil A is changed will some current be induced in the coil
B? Give reason.
Ans. The current if changed in coil A. Some current will be induced in
the coil B.
Reason: When the current in coil A is changed, the
magnetic field around it also changes. As the coil B is placed very close to
the coil A, the magnetic field lines around B coil also changes due to this as
current is induced in it.
15. State the rule to determine the direction of a
(i) magnetic field produced
around a straight conductor carrying current.
(ii) force experienced by a
current-carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is
perpendicular to it, and
(iii) current induced in a
coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field.
Ans. (i) To know the direction of magnetic field produced around a
straight conductor-carrying current. Rule used is-Right hand thumb rule’.
(ii) Fleming’s left hand rule
is used to find the direction of force experienced by a current carrying
straight conductor, when placed in a magnetic field, which is perpendicular to
it.
(iii) Fleming’s right hand
rule is used to determine the direction of current induced in a coil due to its
rotation in a magnetic field.
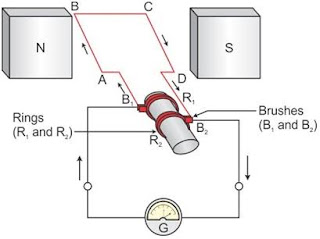
16. Explain the underlying principle and working of an electric
generator by drawing a labelled diagram. What is the function of brushes?
Ans.
Principle: An
electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a
coil is rotated between the magnet or when the magnet is rotated in and out of
the coil the current is induced in the coil and the direction of current is
given by Fleming’s right hand rule.
Working: As shown
in the figure, when the axle attached to the two rings is rotated such that arm
AB moves up and arm CD moves down in the magnetic field produced by the
permanent magnet i.e. ABCD rotates clockwise. By Fleming’s right hand rule, the
induced currents are set up in these arms and flows in the direction ABCD,
which flows from B2 to B.
After half a rotation, arm CD
starts moving up and AB moves down. As the directions of the induced currents
in both the arms change current is induced in direction DCBA, which further
flows from Bl to B2 externally. After every half rotation the polarity of the
current in arms changes. Such current which changes direction after equal
intervals of time is called an alternating current (AC).
Brushes: are used
to transmit current induced externally from coil ABCD to the external circuit.
17. When does an electric short circuit occur?
Ans. When the insulation of a wire gets damaged and this naked wire
comes in contact with other such wire i.e. live wire and neutral wire comes in
contact, the current flowing in the circuit rises and short circuiting occurs.
18. What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary
to earth metallic appliances?
Ans. The earth wire is connected as a safety measure with all
electrical appliances that have metallic body e.g., microwave, electric press,
toaster, geyser, cooler, AC, etc. The earth wire provides a low resistance
conducting path for electric current. If there is any leakage of current then
the user would not get any current because the current flows down into the
earth and keeps the potential of the appliance and earth same.






Sir I am ur tution ka bacha
ReplyDeleteOr k hall sirrrrr
ReplyDeleteReply to krdo sirrrrr
ReplyDeleteNaraj ho kya sirrrrrrr
ReplyDeleteFor class 10th science complete chapter wise mock test visit
ReplyDeleteFree Online MCQs on Class 10th Science
Thanks For Sharing Such an informatove post, Good work and great Stuff. Access us to know more about Magnets.
ReplyDeleteMagnetic Destoner Manufacturers
Circular Magnet Manufacturers
Magnetic Roll Manufacturers
Industrial Magnet Manufacturers
Vibro Separator Manufacturers