Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Diffraction Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) designed specifically to help you succeed in the HTET 2023. The HTET is a significant milestone in your teaching career, and understanding complex topics like diffraction is crucial. In this blog, we'll delve into the fascinating world of wave phenomena and provide you with a set of MCQs that will not only test your knowledge but also enhance your understanding of diffraction. Let's get started on your journey to mastering this topic!
1. What is diffraction in the context of wave physics?
A)
The
bending of light as it passes through a medium
B)
The
reflection of waves off a surface
C)
The
spreading of waves as they encounter an obstacle or aperture
D)
The
interference of two waves to form a new wave
2. Which type of waves can undergo diffraction?
A)
Only
mechanical waves
B)
Only
electromagnetic waves
C)
Both
mechanical and electromagnetic waves
D)
Neither
mechanical nor electromagnetic waves
3. What happens to the angle of diffraction when the
wavelength of a wave decreases?
A)
The
angle of diffraction increases
B)
The
angle of diffraction decreases
C)
The
angle of diffraction remains the same
D)
The
angle of diffraction depends on the medium
4. Which factor primarily determines the amount of
diffraction that occurs when a wave encounters an obstacle?
A)
Wave
frequency
B)
Wave
velocity
C)
Wavelength
of the wave
D)
Wave
amplitude
5. What is the name for the pattern of dark and light
bands formed when light undergoes diffraction by a single slit or aperture?
A)
Fresnel
pattern
B)
Newton's
rings
C)
Diffraction
pattern
D)
Interference
pattern
6. In which of the following situations is diffraction
most pronounced?
A)
When
light passes through a wide slit
B)
When
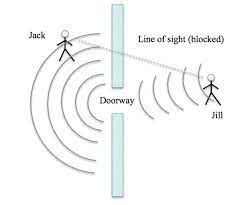
sound waves pass through a narrow doorway
C)
When
radio waves encounter a metal surface
D)
When
water waves encounter a deep ocean
7. What is the phenomenon where two waves of the same
frequency and amplitude interfere constructively when they overlap?
A)
Reflection
B)
Refraction
C)
Diffraction
D)
Interference
8. Which of the following colors of visible light has
the longest wavelength?
A)
Red
B)
Green
C)
Blue
D)
Violet
9. What type of diffraction occurs when waves encounter
a periodic array of closely spaced slits or obstacles?
A)
Single-slit
diffraction
B)
Double-slit
diffraction
C)
Multi-slit
diffraction
D)
Grating
diffraction
10. Which scientist is famous for conducting experiments
with light to study its diffraction and interference properties?
A)
Albert
Einstein
B)
Isaac
Newton
C)
Thomas
Young
D)
Max
Planck
11. Which phenomenon occurs when two waves with the same
frequency and amplitude meet in such a way that they cancel each other out?
A)
Refraction
B)
Interference
C)
Polarization
D)
Dispersion
12. When a beam of white light is incident on a
diffraction grating, what is the result in terms of colors observed?
A)
No
colors are observed; only white light is seen.
B)
All
colors are observed in a continuous spectrum.
C)
Only
the primary colors (red, green, and blue) are observed.
D)
A
single color, such as yellow, is observed.
13. In a single-slit diffraction experiment, if the
width of the slit is decreased, what happens to the diffraction pattern?
A)
The
central maximum gets narrower.
B)
The
central maximum gets wider.
C)
The
number of maxima increases.
D)
The
maxima become dimmer.
14. Which of the following factors affects the amount of
diffraction when waves encounter an obstacle?
A)
The
speed of the waves
B)
The
frequency of the waves
C)
The
size of the obstacle relative to the wavelength
D)
The
phase of the waves
15. Which type of wave experiences diffraction when
passing through an aperture, such as a small opening in a wall?
A)
Sound
waves
B)
Radio
waves
C)
Light
waves
D)
All
of the above
16. In a double-slit interference and diffraction
experiment with light, what pattern is observed on the screen when both slits
are open?
A)
A
single bright band
B)
A
series of bright and dark bands
C)
No
pattern, just a uniform illumination
D)
A
circular pattern
17. What is the primary difference between interference
and diffraction?
A)
Interference
occurs with one wave, while diffraction involves two waves.
B)
Diffraction
is the bending of waves around obstacles, while interference is the interaction
of waves.
C)
Interference
occurs only with electromagnetic waves, while diffraction occurs with all types
of waves.
D)
Diffraction
occurs only with sound waves, while interference occurs with light waves.
18. When a laser beam passes through a narrow slit, what
happens to the width of the central maximum in the resulting diffraction
pattern as the slit width decreases?
A)
The
width of the central maximum increases.
B)
The
width of the central maximum decreases.
C)
The
width of the central maximum remains the same.
D)
The
central maximum disappears.
19. Which physicist is known for his contributions to
the understanding of diffraction and interference of X-rays and electrons?
A)
Isaac
Newton
B)
Max
Planck
C)
Albert
Einstein
D)
Louis
de Broglie
20. What is the phenomenon where light waves change
direction as they pass from one medium to another due to a change in speed?
A)
Diffraction
B)
Dispersion
C)
Refraction
D)
Reflection
21. Which of the following types of waves is most commonly associated with diffraction?
A) Longitudinal waves
B) Transverse waves
C) Electromagnetic waves
D) Surface waves
22. When a sound wave encounters an obstacle, what type of diffraction is typically observed?
A) Single-slit diffraction
B) Double-slit diffraction
C) Grating diffraction
D) No diffraction occurs with sound waves.
23. Which of the following factors affects the degree of diffraction for a given wave?
A) The amplitude of the wave
B) The wavelength of the wave
C) The frequency of the wave
D) The wave's speed
24. In a double-slit experiment with light, what happens to the spacing between interference fringes (bright and dark bands) on the screen when the distance between the slits is increased?
A) The spacing between fringes decreases.
B) The spacing between fringes remains the same.
C) The spacing between fringes increases.
D) The fringes disappear.
25. When a wave encounters a sharp edge or a slit, what characteristic of the wave is most affected?
A) Wave frequency
B) Wave velocity
C) Wave polarization
D) Wavefront shape
26. Which type of diffraction pattern is produced when monochromatic light passes through a single slit?
A) A single bright line
B) A series of bright and dark lines
C) A continuous spectrum
D) A series of concentric circles
27. Which scientist is known for his double-slit experiment that provided evidence of the wave-particle duality of light?
A) Thomas Young
B) Max Planck
C) Albert Einstein
D) Niels Bohr
28. What happens to the diffraction pattern when the wavelength of a wave is decreased?
A) The diffraction pattern becomes narrower.
B) The diffraction pattern becomes broader.
C) The diffraction pattern remains unchanged.
D) The diffraction pattern becomes less intense.
29. In which of the following scenarios is diffraction most noticeable?
A) A large wavelength encounters a small slit
B) A small wavelength encounters a large slit
C) A large amplitude wave encounters an obstacle
D) A low-frequency wave encounters a sharp edge
30. What is the phenomenon where a wave encounters multiple obstacles or slits, resulting in complex patterns of interference and diffraction?
A) Single-slit diffraction
B) Double-slit diffraction
C) Multiple-slit diffraction
D) Grating diffraction
31. Which type of waves exhibit the most significant diffraction when encountering obstacles or slits?
A) High-frequency waves
B) Low-frequency waves
C) Short-wavelength waves
D) Long-wavelength waves
32. When a wave passes through a single narrow slit, what characteristic of the diffraction pattern is associated with the central maximum?
A) It is the brightest part of the pattern.
B) It is the darkest part of the pattern.
C) It has the highest frequency.
D) It has the shortest wavelength.
33. What is the name of the phenomenon that occurs when the edges of a solid object cause diffraction of waves, such as sound waves?
A) Snell's law
B) Huygens' principle
C) The Doppler effect
D) Edge diffraction
34. In a double-slit experiment with monochromatic light, if the distance between the two slits is halved, what happens to the interference pattern on the screen?
A) The pattern remains unchanged.
B) The pattern becomes less distinct.
C) The pattern becomes wider.
D) The pattern disappears.
35. Which physicist formulated Huygens' principle, which describes how waves propagate and explains the phenomenon of diffraction?
A) Isaac Newton
B) Thomas Young
C) Christiaan Huygens
D) Albert Einstein
36. What is the primary reason that X-rays are commonly used in diffraction experiments to study crystal structures?
A) X-rays have short wavelengths.
B) X-rays are easy to produce.
C) X-rays are inexpensive.
D) X-rays are less hazardous than other forms of radiation.
37. When a wave encounters a small obstacle, what happens to the intensity of the wave in the shadow region behind the obstacle?
A) It increases.
B) It remains the same.
C) It decreases.
D) It depends on the shape of the obstacle.
38. Which type of diffraction pattern is produced when a wave encounters a periodic array of evenly spaced slits or obstacles?
A) Single-slit diffraction
B) Double-slit diffraction
C) Grating diffraction
D) Multiple-slit diffraction
39. What is the phenomenon where waves traveling through a narrow opening or slit spread out as they exit the aperture, creating a diverging pattern?
A) Refraction
B) Interference
C) Diffraction
D) Dispersion
40. In a double-slit experiment with electrons, what did the results demonstrate regarding the wave-particle duality of electrons?
A) Electrons behave solely as particles.
B) Electrons behave solely as waves.
C) Electrons exhibit both particle and wave-like behavior.
D) Electrons do not participate in interference.
41. Which type of diffraction pattern is typically observed when waves encounter a circular aperture or obstacle?
A) Single-slit diffraction
B) Double-slit diffraction
C) Grating diffraction
D) Circular diffraction
42. When monochromatic light passes through a single narrow slit, what happens to the width of the central maximum (central bright band) if the wavelength of the light is increased?
A) The width of the central maximum increases.
B) The width of the central maximum decreases.
C) The width of the central maximum remains the same.
D) The central maximum disappears.
43. Which scientist is known for his experiments with water waves that provided early evidence of diffraction and interference phenomena?
A) Isaac Newton
B) Christiaan Huygens
C) Thomas Young
D) Albert Einstein
44. When a wave encounters an obstacle or aperture that is much smaller than the wavelength, what type of diffraction occurs?
A) Single-slit diffraction
B) Double-slit diffraction
C) Fraunhofer diffraction
D) Rayleigh diffraction
45. In a double-slit experiment with light, what happens to the interference pattern on the screen when the distance between the screen and the double slits is increased?
A) The pattern becomes more intense.
B) The pattern becomes less distinct.
C) The pattern becomes wider.
D) The pattern remains the same.
46. What is the phenomenon where a wavefront of light is altered in shape as it passes through an opening or encounters an obstacle?
A) Refraction
B) Polarization
C) Diffraction
D) Dispersion
47. Which of the following types of waves exhibits the least diffraction when encountering obstacles?
A) Longitudinal waves
B) Transverse waves
C) Electromagnetic waves
D) Surface waves
48. What is the name for the phenomenon where the diffraction of waves causes the spreading out of waves in all directions from an opening or obstacle?
A) Huygens' principle
B) Rayleigh scattering
C) Spherical diffraction
D) Fraunhofer diffraction
49. In a double-slit experiment with electrons, what do the results demonstrate regarding the wave-particle duality of electrons?
A) Electrons behave solely as particles.
B) Electrons behave solely as waves.
C) Electrons exhibit both particle and wave-like behavior.
D) Electrons do not participate in interference.
50. Which of the following factors primarily determines the degree of diffraction when a wave encounters an obstacle?
A) Wave frequency
B) Wave speed
C) Wavelength of the wave
D) Wave amplitude
In conclusion, preparing for the Diffraction section of the HTET 2023 requires a solid grasp of wave behaviors and their interactions with obstacles. These carefully curated MCQs are designed to help you strengthen your knowledge and test-taking skills. Remember to practice regularly, review your answers, and seek further clarification on any challenging concepts. With dedication and effective study strategies, you can confidently approach the HTET exam and demonstrate your expertise in science and teaching. Best of luck with your preparations and success in the upcoming HTET 2023!





No comments:
Post a Comment